AI Summary
Alibaba's Qwen3 is an AI model family that rivals OpenAI and Google, with performance rivaling or surpassing industry leaders. Its hybrid architecture allows for "thinking" and "non-thinking" modes, enabling faster response times and accurate fact-checking. The models utilize Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, achieving remarkable performance while using fewer computational resources, making them more cost-effective for production environments.
Alibaba has just unleashed its newest AI model family
Qwen3, with performance that rivals and sometimes surpasses offerings from industry leaders like OpenAI and Google. Let's dive into what makes this release particularly noteworthy in today's competitive AI landscape.
The Rise of Qwen3: What Makes It Special
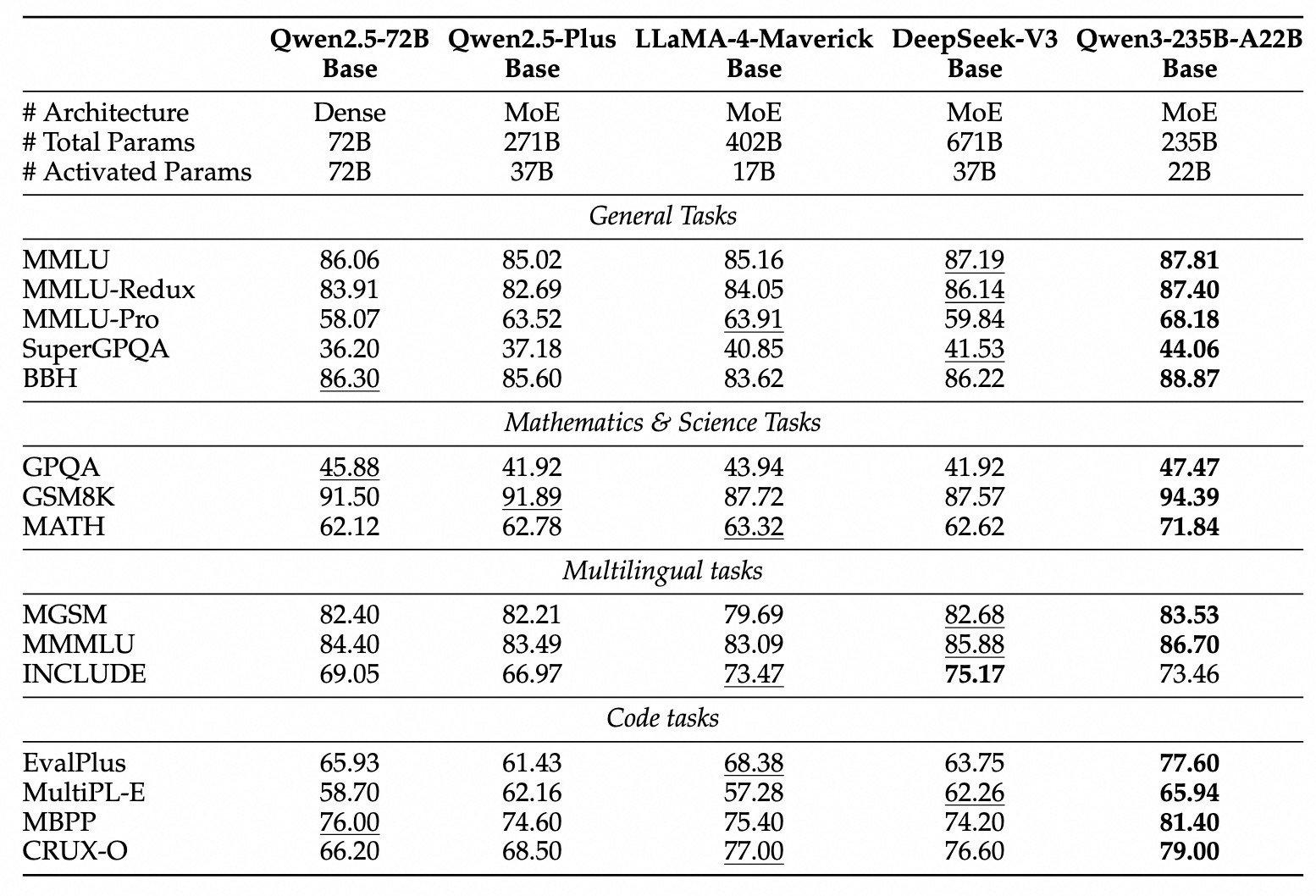
Alibaba's latest addition to its AI portfolio, Qwen3, represents a substantial evolution in large language model technology. Released on April 29, 2025, this new family of models comes in various sizes, ranging from a compact 0.6 billion parameters to a massive 235 billion parameters. While parameter count isn't the only measure of an AI model's capabilities, it generally correlates with problem-solving abilities and overall performance.
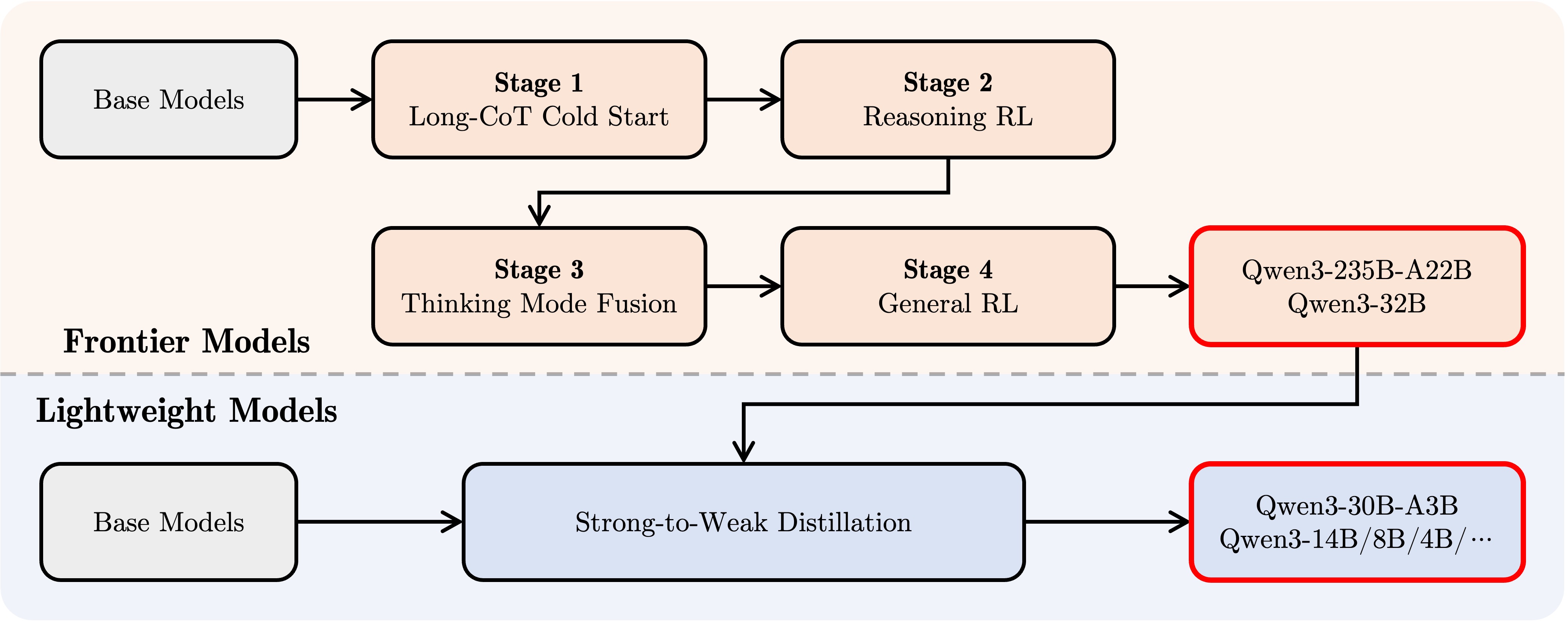
What sets Qwen3 apart is its hybrid architecture that incorporates both "thinking" and "non-thinking" modes. This dual approach allows the models to:
- Take time to reason through complex problems step-by-step when accuracy is paramount
- Respond quickly to simpler queries when speed matters more than depth
- Effectively self-check facts, similar to OpenAI's o3 models
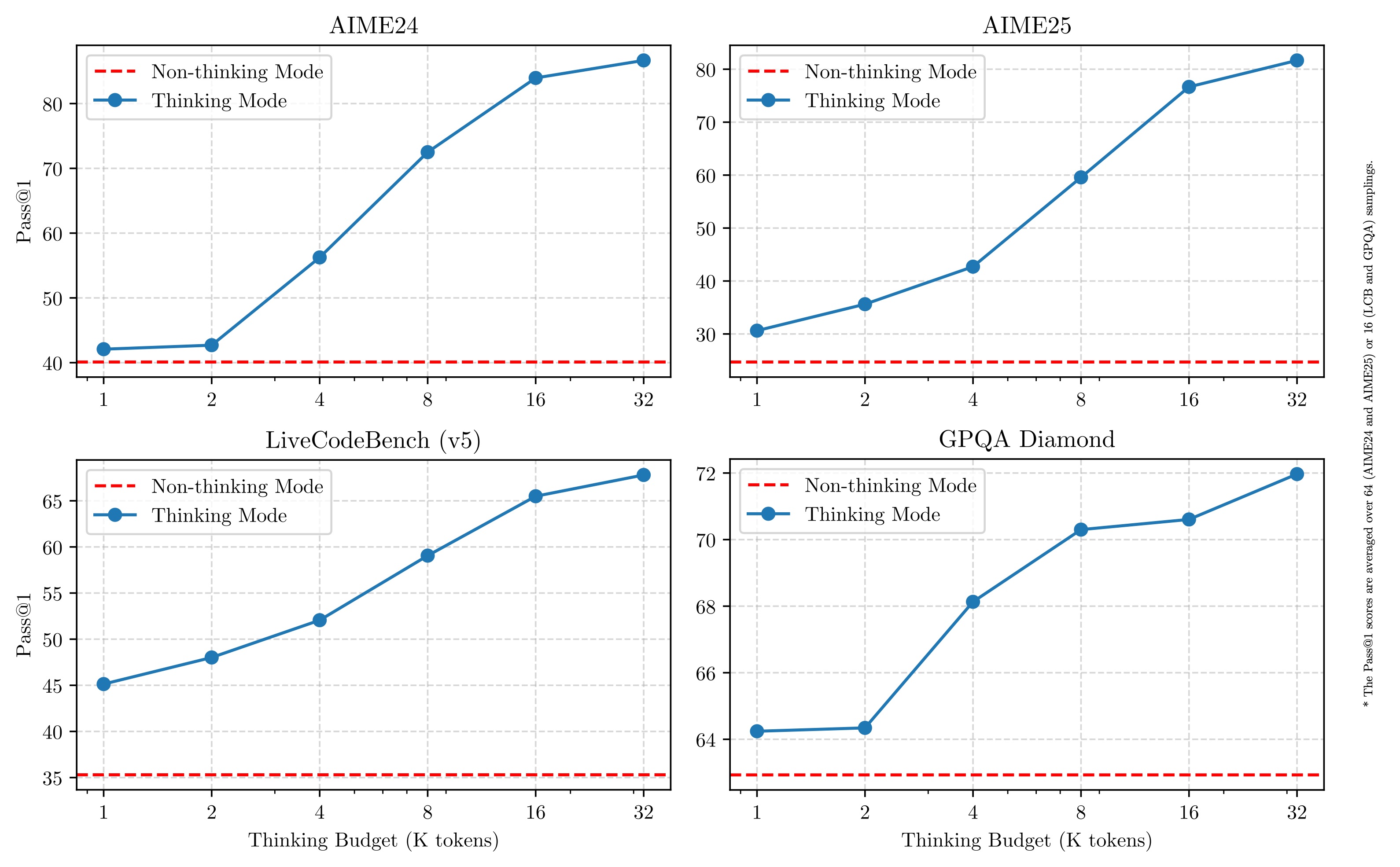
- Allow users to control the "thinking budget" based on their specific needs
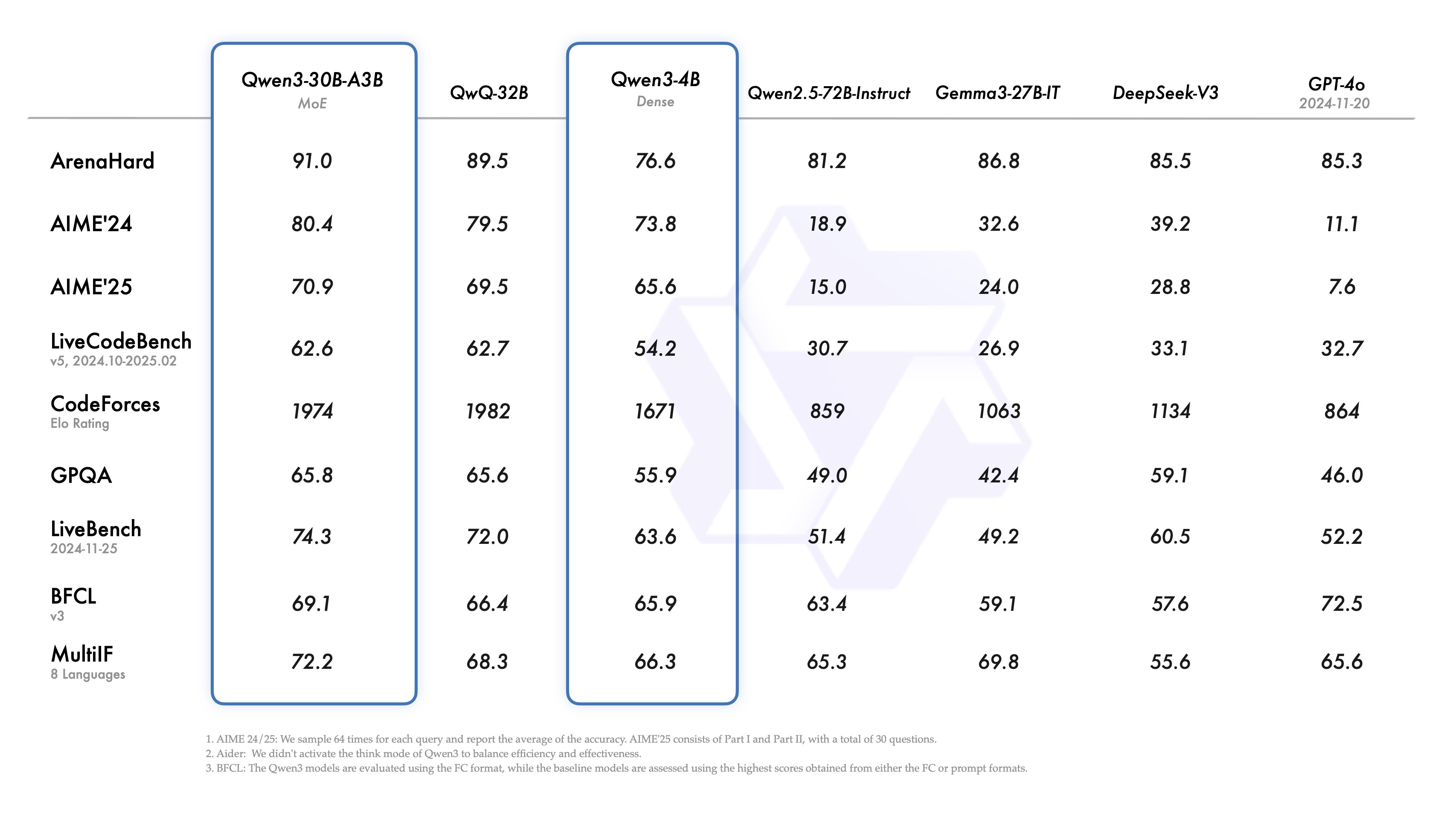
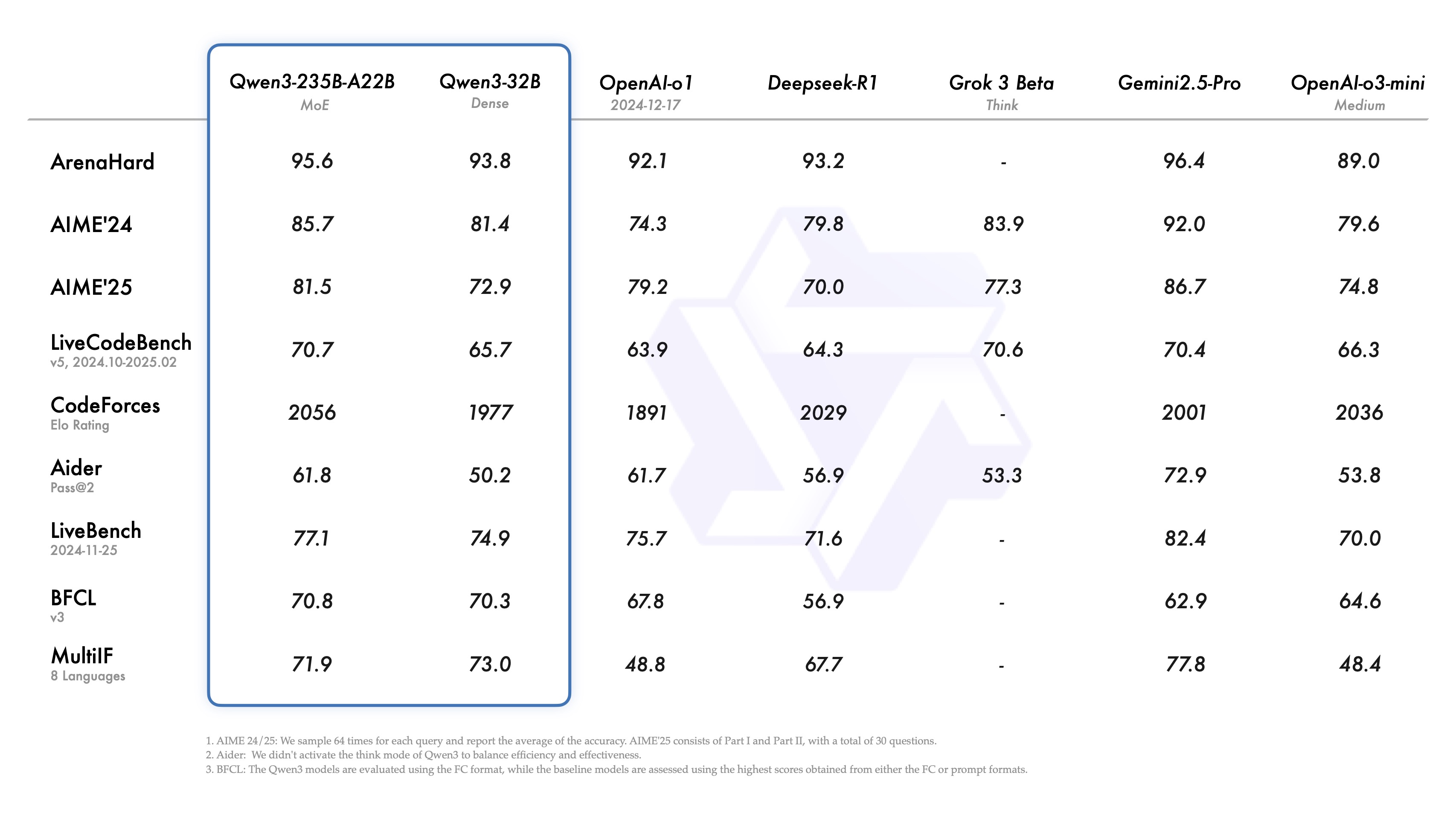
The largest model in the family, Qwen3-235B-A22B, has demonstrated impressive performance in benchmarks, beating out competitors like OpenAI's o3-mini and Google's Gemini 2.5 Pro in certain tests.
Mixture of Experts: Smarter AI Architecture
Some of the Qwen3 models utilize a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, which represents an innovative approach to AI design that focuses on computational efficiency. Unlike traditional "dense" models where all parameters work on every task, MoE models:
- Break down complex tasks into specialized subtasks
- Delegate these subtasks to smaller "expert" models
- Activate only the relevant parameters needed for a specific query
The two MoE models in the Qwen3 family are:
- Lightweight Qwen3-30B-A3B Model: 30 billion total parameters with 3 billion activated parameters
- Frontier Qwen3-235B-A22B Model: 235 billion total parameters with 22 billion activated parameters
This approach allows Qwen3 to achieve remarkable performance while using significantly fewer computational resources during inference, making it more cost-effective to run in production environments.
Training Data and Multilingual Capabilities
Alibaba didn't skimp on training data for Qwen3. The models were trained on an impressive dataset of nearly 36 trillion tokens—nearly twice the size used for the previous Qwen2.5 models. To put this in perspective, 36 trillion tokens would be equivalent to about 27 trillion words, representing an enormous corpus of knowledge.
The training data includes:
- Textbooks and educational material
- Question-answer pairs for improved reasoning
- Code snippets to enhance programming abilities
- AI-generated synthetic data
- PDF-like documents processed by earlier Qwen models
Perhaps most impressively, Qwen3 supports 119 languages and dialects, making it one of the most linguistically diverse AI models available. This extensive language support opens up global applications and makes the technology accessible to users worldwide.
Benchmark Performance: How Does It Stack Up?
While no single AI model dominates across all benchmarks, Qwen3 shows impressive performance across multiple domains:
- Coding: On Codeforces, Qwen3-235B-A22B slightly outperforms OpenAI's o3-mini and Google's Gemini 2.5 Pro
- Mathematics: It beats o3-mini on the challenging AIME benchmark
- Reasoning: Shows superior performance on the BFCL test for logical reasoning
The publicly available Qwen3-32B model remains competitive with several proprietary and open AI models, including Chinese AI lab DeepSeek's R1, and surpasses OpenAI's o1 model on several tests, including the coding benchmark LiveCodeBench.
Open Access and Availability
One of the most significant aspects of the Qwen3 release is its accessibility. Most of the models in the Qwen3 family are available for download under an open license from AI development platforms like Hugging Face and GitHub. You can also try out the Qwen3-demo on Hugging Face
here. This open approach contrasts with the closed-source strategies employed by companies like OpenAI and Anthropic.The dense models available under Apache 2.0 license include:
For deployment, users can leverage frameworks like SGLang and vLLM, or use tools such as Ollama, LMStudio, and llama.cpp for local usage. Qwen3 is also available through cloud providers including Fireworks AI and Hyperbolic.
Qwen3's architecture and capabilities make it suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Software Development: Its strong coding abilities make it valuable for programming tasks and code generation
- Mathematical Problem-Solving: The models excel at complex mathematical reasoning
- Multilingual Applications: Support for 119 languages enables global deployment
- Agentic Capabilities: Qwen3 excels at tool-calling and can follow instructions precisely
For developers interested in experimenting with Qwen3, getting started is straightforward. The models can be run locally using Ollama with simple commands like:
ollama run qwen3:8b
Or for the 30B MoE models:
ollama run qwen3:30b-a3b
Note that the Qwen project is also releasing quantized versions of its Qwen3 models with AWQ and GGUF formats for the Qwen3-14B and Qwen3-32B models. This release is specifically aimed at allowing users with limited GPU memory to utilize these models. When using the GGUF formats in applications like Ollama and LMStudio, users can employ the special token "/no_think" to user prompts or system messages to switch the model's thinking mode from thinking to non-thinking modes.
The Geopolitical Context
The release of Qwen3 comes at a time of increasing technological competition between China and the United States. As Chinese AI models like Qwen3 continue to demonstrate capabilities on par with or exceeding those of American counterparts, the pressure intensifies on U.S. labs to accelerate their development efforts.
This technological race has significant geopolitical implications, leading U.S. policymakers to implement restrictions on the export of advanced chips that could be used for AI training to Chinese companies. Despite these challenges, Alibaba has managed to develop a suite of models that remain competitive in the global AI landscape.
Adding to this competitive dynamic, Huawei Technologies is reportedly preparing to test its newest and most powerful artificial-intelligence processor. According to the
Wall Street Journal, Huawei's new Ascend 910D chip aims to replace some higher-end products from U.S. chip giant Nvidia, potentially offering performance that exceeds Nvidia's H100. The first batch of samples could be available as early as late May 2025, with Huawei already approaching Chinese tech companies to test the technical feasibility of the new processor.
This development is particularly significant given that Washington has cut China off from Nvidia's most advanced AI products, including the H100 chip (banned before it even launched in 2022) and the newer flagship B200 chip. These restrictions are part of a broader U.S. strategy to limit China's technological development, particularly advances that could benefit its military capabilities.
Huawei and other Chinese tech companies have struggled for years to match Nvidia in building top-end chips for training AI models, but recent developments suggest the gap may be narrowing. Combined with the release of advanced AI models like Qwen3, these hardware advancements signal China's determination to achieve technological self-sufficiency in the face of U.S. restrictions.
As Tuhin Srivastava, co-founder and CEO of AI cloud host Baseten, noted: "The U.S. is doubling down on restricting sales of chips to China and purchases from China, but models like Qwen3 that are state-of-the-art and open... will undoubtedly be used domestically. It reflects the reality that businesses are both building their own tools [as well as] buying off the shelf via closed-model companies like Anthropic and OpenAI."
What This Means for the Future of AI
Alibaba's Qwen3 release represents another significant step in the democratization of advanced AI capabilities. As open-source models continue to improve and compete with proprietary systems, we're likely to see:
- More widespread adoption of powerful AI capabilities across industries
- Increased competition driving further innovation in model architecture and training techniques
- Greater accessibility of advanced AI for developers and organizations with limited resources
- Continued blurring of lines between open and closed AI ecosystems
Qwen3 demonstrates that the gap between open-source and proprietary AI models is narrowing, challenging the notion that cutting-edge AI capabilities must remain behind closed doors. With its hybrid thinking modes, MoE architecture, and support for 119 languages, Qwen3 offers a compelling alternative to proprietary models from companies like OpenAI and Google. This trend could fundamentally reshape the AI landscape in the coming years, potentially accelerating the development of increasingly capable AI systems while making them more accessible to a broader range of users.
Qwen Chat:
https://chat.qwen.ai/Github:
https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3Hugging Face:
https://huggingface.co/collections/Qwen/qwen3-67dd247413f0e2e4f653967fModelscope:
https://modelscope.cn/collections/Qwen3-9743180bdc6b48Kaggle:
https://www.kaggle.com/models/qwen-lm/qwen-3Demo:
https://huggingface.co/spaces/Qwen/Qwen3-DemoRecent Posts