AI Summary
Ford is leveraging DeepSeek's open-source AI technology to transform its design process, aiming to compete with Chinese automakers that have shortened their engineering cycles. By using AI agents and advanced GPU technology, Ford hopes to accelerate aspects of the design process, including converting 2D sketches into 3D models and predicting stresses and physics-based tests, reducing simulation times by up to 90%.
In the fast-paced world of automotive design, Ford Motor Company is betting big on AI to help it compete in an increasingly challenging market. Bryan Goodman, Ford's director of artificial intelligence, recently shared insights into the company's AI strategy at
NVIDIA's GTC event in San Jose during NVDIA GTC event, highlighting how AI agents and advanced GPU technology are transforming their design process.
Why Ford Needs to Speed Up
"We have to speed up to be competitive," Goodman told the
Wall Street Journal at the event. With Chinese automakers dramatically shortening their engineering cycles and Ford facing challenges including sluggish EV demand, rising competition, and new U.S. tariffs, the pressure is on to innovate faster.
Despite his confidence that "Ford engineers as good of products as anyone in the world in automotive," Goodman emphasized that speed is now critical to maintaining competitiveness. This urgency comes after Ford's disappointing 2025 outlook caused shares to fall last month, despite higher fourth-quarter revenue.
Transforming the Clay Model Process
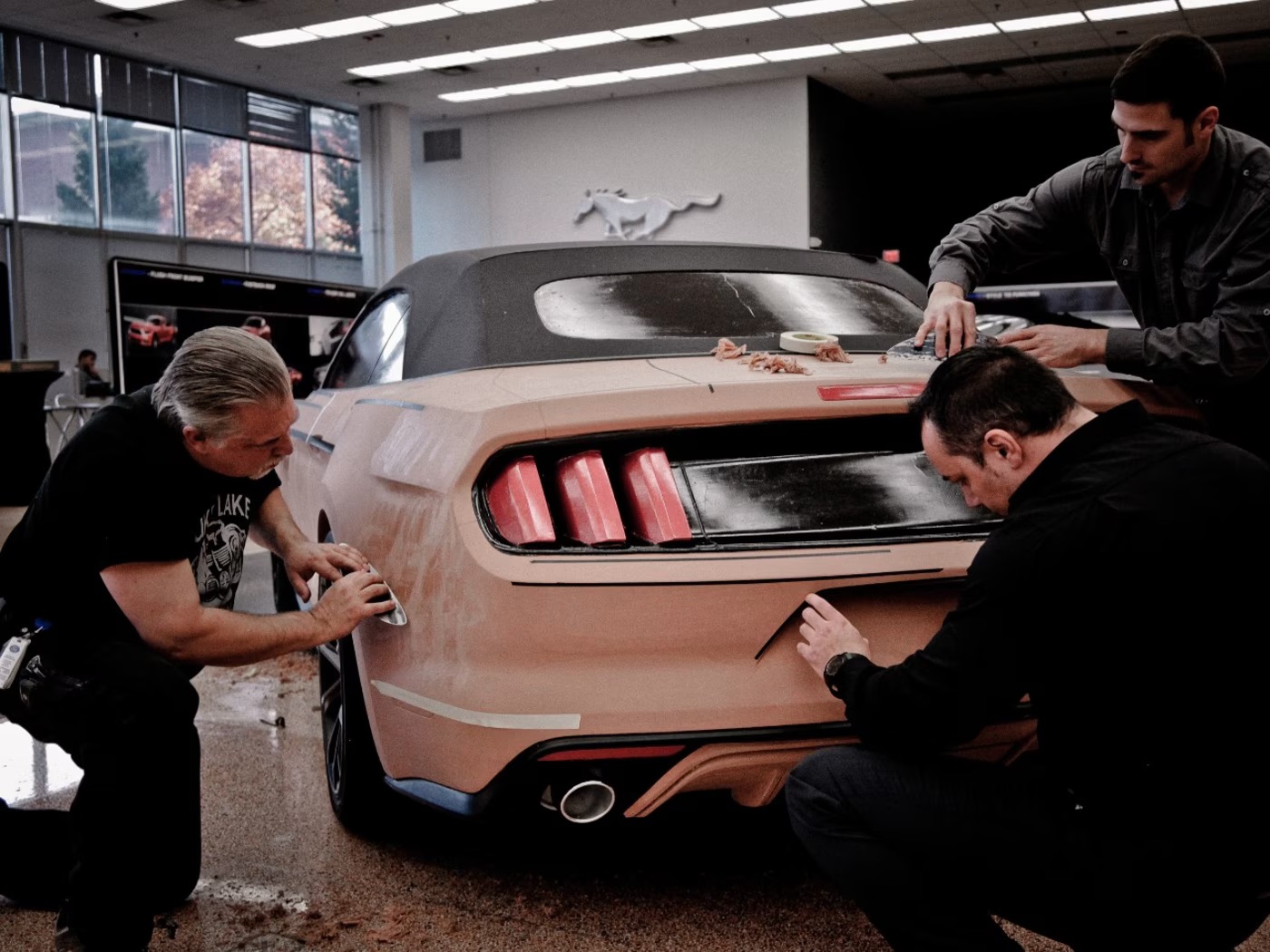
One of Ford's most ambitious AI applications targets the company's traditional design process. Currently, designers sculpt each new model out of clay before handing it off to engineers for simulations and stress tests—a process Goodman describes as "very time consuming." Ford is using AI to dramatically accelerate aspects of this process. The company has developed systems that can:
- Convert 2D sketches into 3D models and renderings
- Connect design work directly with engineering processes
- Predict stresses and physics-based tests that traditionally take hours
- Reduce 15-hour computational fluid dynamics simulations to just 10 seconds
When asked about the distinction between simple AI models and true AI agents, Goodman explained that Ford is stringing together multiple AI capabilities to create more autonomous systems. "The agent might be rendering and then creating a 3D model and then doing a stress analysis on it. That's where I view this as agentic," he said.
This approach allows AI to handle increasingly complex sequences of tasks with less human intervention, potentially removing bottlenecks in the design process.
Ford's AI Ecosystem: From OpenAI to DeepSeek
Ford isn't putting all its eggs in one basket when it comes to AI models. Goodman revealed that the company uses a diverse range of AI systems, including those from OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, Meta, Mistral, and DeepSeek (a Chinese AI company).
Interestingly, Goodman specifically mentioned DeepSeek, noting that while it's "very good," he doesn't see it as "any better than the latest Anthropic and [Google] Gemini and OpenAI models." What makes DeepSeek valuable to Ford is its open-source nature, which Goodman believes will foster innovation: "Because they shared everything with the world, I think we're going to see a lot built on top of it."
Unlike many companies that have moved their AI operations to the cloud, Ford maintains a substantial in-house GPU infrastructure—"a few thousand" Nvidia GPUs, according to Goodman.
This approach stems from Ford's experience with cloud-based GPU computing, which Goodman described as "crazy expensive and also just difficult to get." He compared securing cloud GPU capacity to buying "Taylor Swift tickets," noting that sometimes it simply wasn't available at any price.
The Blackwell Conundrum: Preparing for Next-Gen AI Hardware
Ford hasn't yet received Nvidia's next-generation Blackwell chips, which were a major focus of last year's GTC event but faced manufacturing delays. While Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang suggested that Blackwell makes the previous Hopper generation "essentially useless," Goodman was more measured: "I suspect we'll get a lot of use out of our Hopper GPUs the next few years."
More concerning to Goodman are the infrastructure challenges posed by Blackwell and future Nvidia architectures (Rubin and Feynman). "We're having to do major electrical upgrades just to run Blackwell. And they won't be ready for Rubin and Feynman," he explained.
The power requirements for these advanced chips are so substantial that Ford's data center experts have advised against trying to "future-proof" their facilities. "The experts on data center stuff just say: don't even try because you can't buy it yet," Goodman noted.
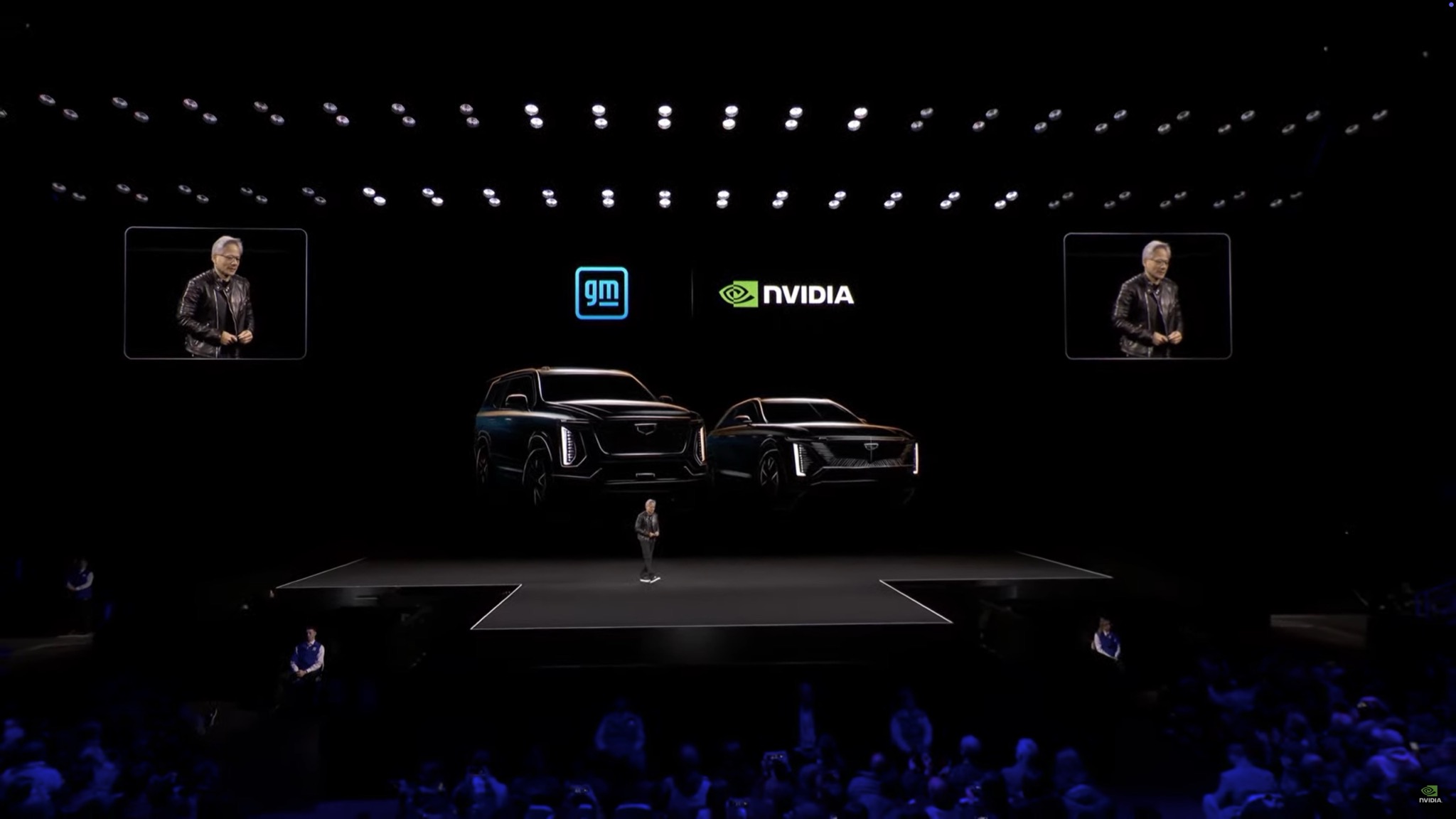
Ford Rival GM Partners With NVIDIA For AI
While Ford continues to expand its AI capabilities, its cross-town rival General Motors is also doubling down on AI through an expanded partnership with NVIDIA. According to recent reports, GM is integrating AI more deeply into its vehicle development and manufacturing processes.
Like Ford, GM is leveraging AI to enhance production efficiency, develop better safety features, and advance smart technologies. The automaker is also looking to incorporate AI more extensively in its autonomous driving technology in the longer term.
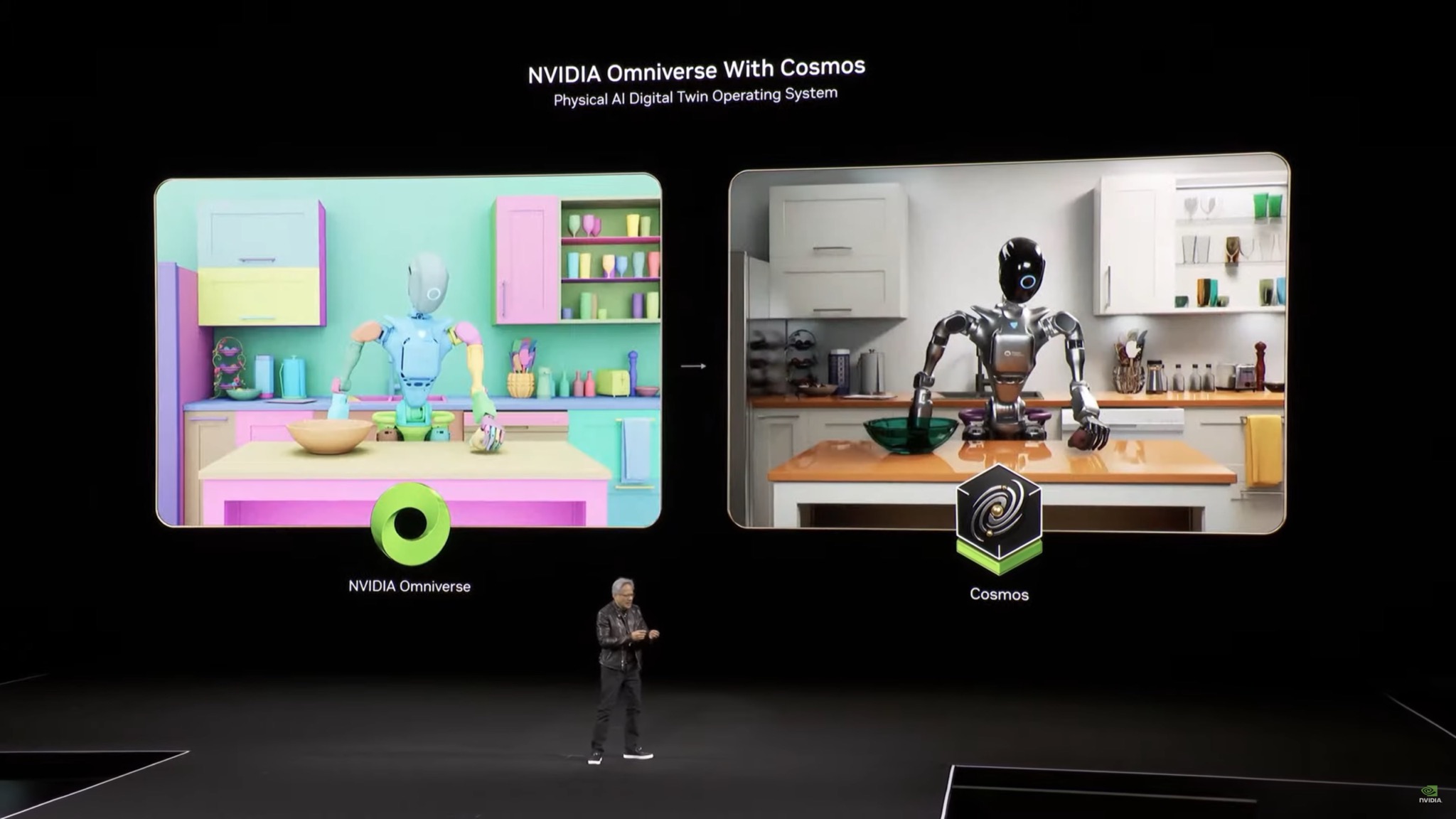
Currently, GM uses NVIDIA's Omniverse and Cosmos platforms to create virtual models of its assembly lines, allowing the company to test new processes and identify potential issues before implementing them in actual plants. This approach helps reduce downtime, cut costs, and improve overall efficiency.
GM is also deploying AI-enabled robots for tasks such as welding, transport, and material handling. Additionally, the company is utilizing NVIDIA DRIVE AGX to enhance its advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
"GM has enjoyed a longstanding partnership with NVIDIA, leveraging its GPUs across our operations," said General Motors CEO Mary Barra. "AI not only optimizes manufacturing processes and accelerates virtual testing but also helps us build smarter vehicles while empowering our workforce to focus on craftsmanship. By merging technology with human ingenuity, we unlock new levels of innovation in vehicle manufacturing and beyond."
What This Means for Ford's Future
Ford's AI strategy represents a significant shift in how the company approaches vehicle design and engineering. By embracing AI agents and investing heavily in GPU infrastructure, Ford is positioning itself to compress development cycles and respond more quickly to market changes.
However, the challenges are substantial. Power requirements for advanced AI hardware are creating infrastructure bottlenecks, and the competitive landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Chinese automakers are setting a blistering pace of innovation, and established players like Ford must transform decades-old processes to keep up.
For consumers, this could mean more frequent model updates and innovations as Ford's AI-powered design process begins to bear fruit. For the industry, it signals that even traditional automakers with long histories are embracing AI not just as a feature in their vehicles, but as a fundamental tool in how those vehicles are conceived, designed, and brought to market.
Recent Posts